In the realm of computer peripherals, the mouse encoder quietly performs an indispensable role, shaping our digital interactions with every subtle movement. Often overlooked, this tiny component is the unsung hero responsible for translating the physical motion of the mouse into precise, responsive actions on the screen. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of mouse encoders, exploring their functions, types, and how they contribute to the overall performance of our beloved mice.
-
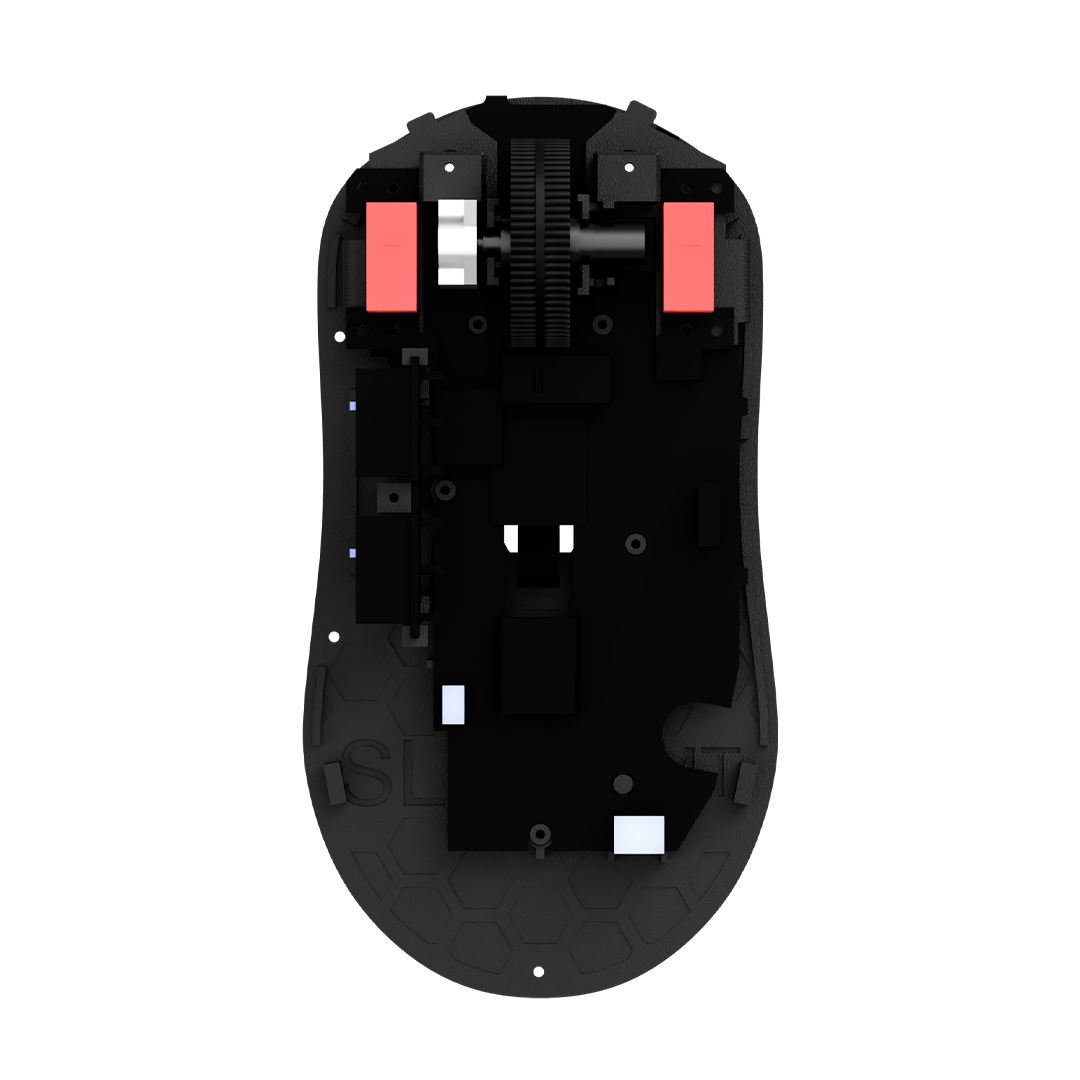
Understanding the Mouse Encoder: At its core, a mouse encoder is a device that converts the rotational movement of the mouse wheel into electrical signals that the computer can interpret. The encoder serves as the bridge between the mechanical motion of scrolling and the digital response on our screens, making it an essential component for both productivity and gaming.
-
Types of Mouse Encoders: a. Mechanical Encoders: Mechanical encoders, the traditional type, use physical components like notched wheels and sensors to detect the rotation of the mouse wheel. While effective, they can be prone to wear and tear over time, potentially leading to a decrease in accuracy and responsiveness.
b. Optical Encoders: Optical encoders, on the other hand, employ infrared light and sensors to detect wheel movement. This type of encoder is often considered more durable than its mechanical counterpart, as it lacks the physical parts that may degrade with prolonged use. Optical encoders contribute to smoother scrolling experiences and are commonly found in modern mice.
-
Incremental vs. Absolute Encoders: a. Incremental Encoders: Incremental encoders measure changes in position, providing information about the direction and speed of rotation. They are commonly used in mice to track relative movement, making them well-suited for scrolling applications.
b. Absolute Encoders: Absolute encoders, less common in mice but prevalent in other applications, provide the exact position of the wheel at any given moment. This precision comes at the cost of increased complexity and a higher price point, making them more niche in the world of consumer mice.
-
Precision and Responsiveness: The quality of a mouse encoder directly influences the precision and responsiveness of the scrolling experience. High-quality encoders ensure that each notch of the wheel corresponds accurately to on-screen movement, offering a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
-
Integration with Other Features: Modern mice often come equipped with additional features that complement the capabilities of the mouse encoder. Adjustable scroll resistance, for example, allows users to customize the feel of their scroll wheel, catering to personal preferences and specific use cases.
Conclusion: As we navigate our digital environments, the mouse encoder quietly works behind the scenes, translating our physical gestures into digital commands. Understanding the nuances of this unassuming yet crucial component empowers users to make informed choices when selecting a mouse that suits their needs. So, the next time you effortlessly scroll through a lengthy document or engage in a precision scroll in your favorite game, take a moment to appreciate the intricate dance of the mouse encoder, elevating your digital experience with every subtle turn of the wheel.




Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.